[inline_ad_block]
At most air-insulated substations, the arrester mounted at the transformer is close enough to other equipment to provide effective protection from flashover. However this applies only if the breakers are closed. If a breaker is open, the insulators on its line side – including its line side bushing – are not protected. In this regard, installing line entrance arresters will protect all points within the station when critical breakers are open – and this applies to all system voltages, including distribution. In fact, because insulation withstand levels are lower at distribution voltages risk becomes even higher. It is worth defining a line entrance arrester since it is possible other names are also being used to describe it. As discussed above, this terminology applies to an arrester mounted on the first structure on an incoming or outgoing line at a substation. About 30% of all substations with breakers are currently equipped with line entrance arresters according to this definition.

CLICK TO ENLARGE
Purpose of Line Entrance Arrester
The basic role of a line entrance arrester is to protect a circuit breaker that is ‘open’ from any lightning surge that enters the station along a connected line. Since it’s generally accepted that breakers on incoming lines are usually not left open for long, one might conclude there is little cause for concern. True, breakers normally remain closed. But if there’s a lightning induced fault on the system, the breaker is called into action to interrupt it. That means it can be open for some 100 ms or longer whenever a line fault occurs. This may seem a short duration yet, when it comes to lightning, it’s quite long. Since most lighting events include multiple strokes, the resulting surge can present itself to the power system with anywhere from 2 to 14 independent surges of different magnitudes, each separated by some 50 to 150 ms.
Open Breaker Scenario 1
This scenario occurs when there is no line entrance arrester installed. The time-lapse below describes the events of a lightning surge on a system with an open breaker:
T0 Surge 1 – 1-100 kA strikes line
T5 ms Fault detected on circuit
T50 ms Breaker opens
T100 ms Surge 2 – 1-15 kA, 50-150 ms between each stroke
T100 ms Surge 2 hits open breaker
T100 ms Bushing flashes over from voltage doubling effect because arrester on transformer is unable to protect it through open breaker.

CLICK TO ENLARGE
Bushing flashover is likely because, when the surge encounters an open circuit, it doubles in magnitude. Fortunately, lighting flashover does not always convert into a power fault since the power frequency voltage is not available on the line at this point. However, a lightning flashover can trigger other flashovers nearby due to localized ionized gas. If it does, there may be considerable resulting damage. By contrast, if a line entrance arrester is installed, the line side of the breaker is protected from flashover even if the breaker is open. The above scenario therefore changes to no flashover at the time subsequent surges enter the substation.
Open Breaker Scenario 2
Another less subtle scenario exists when a peaking generator goes off-line. Since the breaker on the line side of the step-up transformer is used to isolate it, its line side bushing can flashover from the first incoming lightning surge. Basically, as long as a breaker is open, the transformer arrester cannot protect its line side bushing.
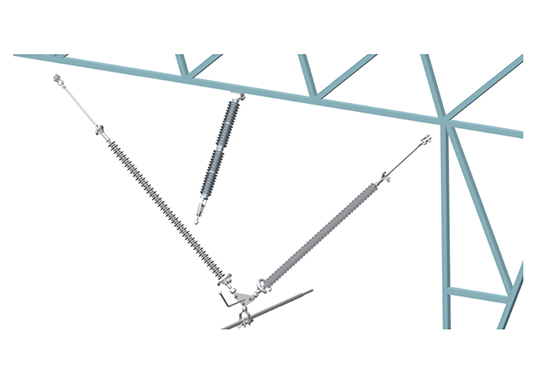
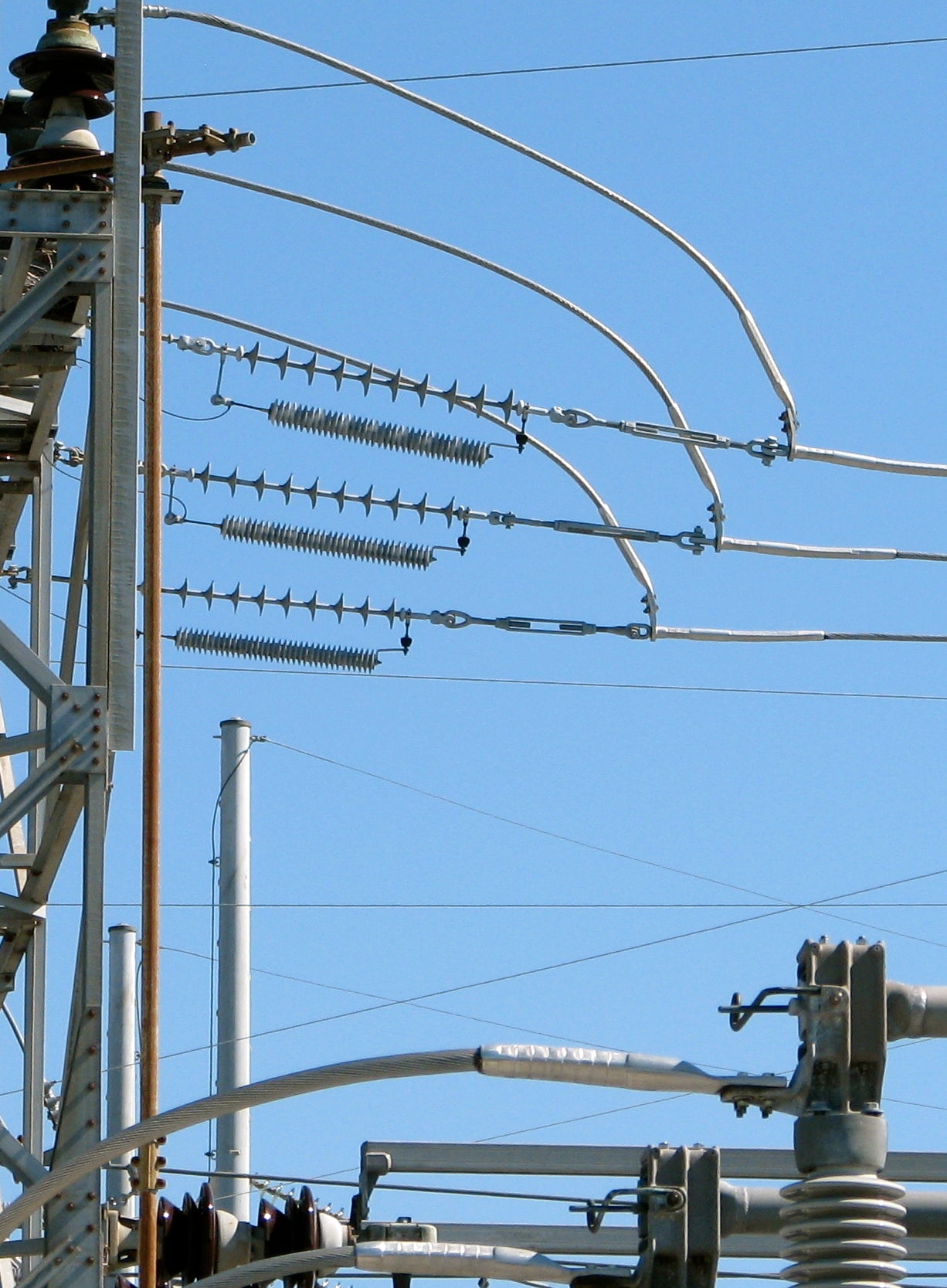
Line Entrance Arrester Configurations
A line entrance arrester can be mounted in just about any configuration and still be effective. For example, locating the arrester close to the breaker is not necessary, although separation distance needs to be taken into account. It should also be noted that an arrester located on the first tower from a station would probably not protect the breaker. The line entrance arrester can even be a transmission line arrester suspended from the first dead end insulator. And, if there’s still doubt as to the value of investing in this type of arrester, just consider the cost of replacing a breaker.
Jonathan Woodworth