Coming at the 2025 INMR WORLD CONGRESS
Replacing old porcelain cap & pin type insulators with modern glass cap & pin discs or long rod composite insulators has become a common upgrade among transmission systems worldwide. The aim has been to enhance performance and reliability while also ensuring long-term cost-effectiveness.
To optimize such a strategy and to prioritize which batches need to be replaced on a priority basis, an inspection-based maintenance approach needs to be adopted.
As a case study of such an approach, a condition assessment program was implemented in Australia to evaluate in-service insulators based on several factors:
• pollution
• ageing
• corrosion, and
• electrical and mechanical performance.
Using the data gathered from these types of assessment, practical recommendations can be made for managing and maintaining the broader insulator fleet.

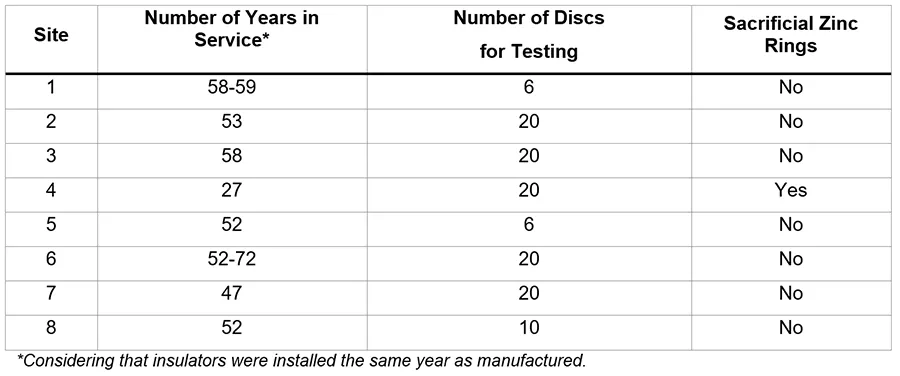
The test array in this case comprised 122 single insulator discs (see Table 1). These were removed from eight different sites. All insulators were produced by the same manufacturer and year of production varied from 1950 to 1995.
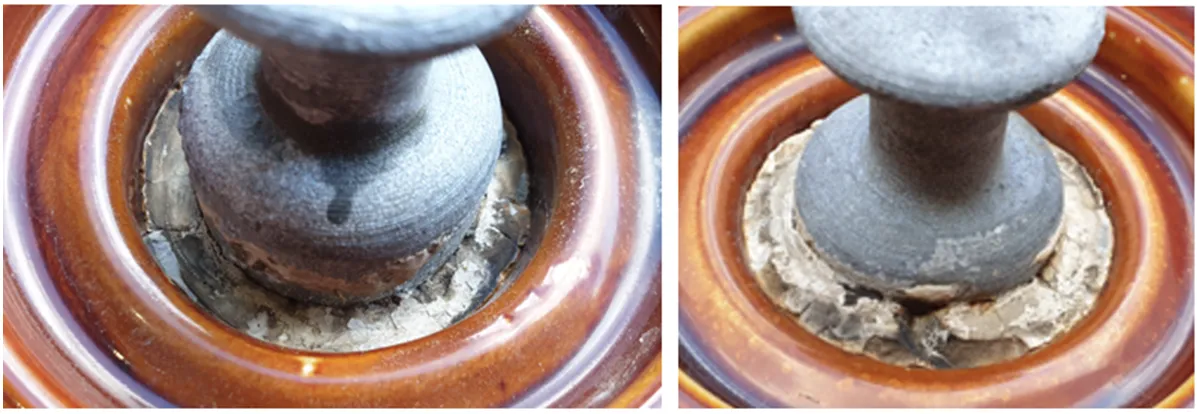

A test program was developed which consisted of the following:
• Visual inspection of all insulators;
• Local pollution measurements at the most polluted parts (around the pin) of some insulators;
• Resistance measurements of single discs for all insulators;
• Impulse puncture testing in air for some selected units from each batch;
• Electro-mechanical failing load test for all insulators;
• Porosity test for some selected units from each batch.
Plan to attend the 2025 INMR WORLD CONGRESS in Panama where insulator expert, Dr. Igor Gutman, will report the findings of this important research program. Dr. Gutman will also make recommendations with regards to how such testing can be optimized to make this type of strategic maintenance strategy most cost-effective.
Join Dr. Gutman and over 120 international experts in this area in this major conference and networking event for engineers and other professionals in transmission and distribution.